|
|
|
|
Process is a group of tasks / activities carried out to
reach a (desired) outcome. The government process is any set
of activities performed by a Government that is initiated by
an event, (e.g. Service Request, Event Trigger, transforms
information, materials or business commitments and produces
an output (delivery of Service to Citizen /Business of
Government).
Government Process Re-engineering (GPR) concept was emerged
from Business Process Re-engineering (BPR) which is defied
as “fundamental rethinking and radical redesign of business
processes to achieve dramatic improvements in critical,
contemporary measures of performance, such as cost, quality,
service and speed”. (Champy, M., & Hammer, J. (1993).
Re-engineering the Corporation: A Manifesto for Business
Revolution.) GPR is based on application of concepts of BPR
to optimize process for the benefits intended.
The introduction of e-Jalseva project as a part
of MWSIP in Water Resources Department is seen as project
arrived at the right time when some reforms are being
articulated by the department. The project is initially
conceived as Management Information System (MIS) for the
entire department and effort was made to create the same. As
awareness about e-Governance percolated in the department
due to officers undergoing various e-Governance capacity
building programmes it was clear that the MIS should be
converted into a full fledge e-Governance project with
bigger role for all the officers and integrating all
processes in the project. While the present version is
created more like a MIS application, lot of insight has gone
while testing the application and it was felt that the
application need to be modified to suit the needs of all the
stakeholders.
Towards, this focused group discussions were carried out at
Koyna Design Circle, Pune and it was articulated that all
the hierarchies should be able to use the system as well as
it needs to be integrated internally within all functional
areas and externally with other applications like Sevarth,
BDS, digital service book, etc. and also with Land records
to reap rich benefits. In order to do that, it is essential
that existing modules of the application be relooked into
and necessary GPR may be initiated in order to make the
application user friendly and all stakeholders can
participate on a day-to-day basis.
|
|
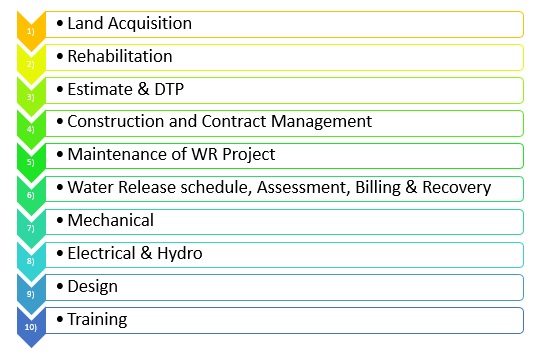
Objectives of GPR:-
|
 The objective of the
GPR is to identify pain areas in the various processes
and functioning of the department in following services
and provide simple, faster, efficient, user friendly to
be process.
The objective of the
GPR is to identify pain areas in the various processes
and functioning of the department in following services
and provide simple, faster, efficient, user friendly to
be process.
|
|
Benefits of GPR:- |
• Simple,
user-friendly, efficient and faster processes
• Uniformity in processes and service deliver throughout
the state.
• Integration and only one time data entry
• Integration with Mobile Gateway for alert mechanism
• The process would be lean and mean.
• It would enable cost and time reduction.
• Provide opportunity for the staff to think and
strategies their work regularly as the process is
streamlined.
• About 60 % of overall work of MWRD would be on e-Jalseva
|
|
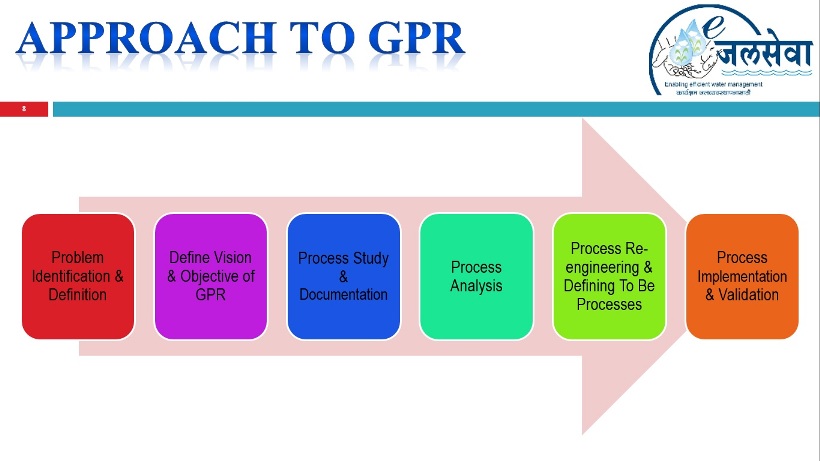
Theoretical Approach to
GPR: |
The theoretical
approach of and various stages that are involved in
performing GPR are depicted as follows-
|
Source: Course Material of EPGP-EG, IIM Indore &
GPR Workshop by NISG at Pune on 07/10/2013
|
The first step in the GPR process is the identification
and statement of the problem in the current process
scenario. This is followed by the definition of the
vision and objectives of GPR. Before setting out on
process reengineering, the existing processes should be
studied and documented. During this phase, data is also
collected from the different processes, to understand
the processes better and to obtain baseline metrics. The
processes thus documented are analyzed using various
tools and methodologies, to identify improvement
opportunities. This will include identification of value
adding / non value adding activities, process complexity
and process metrics. During the re-engineering phase,
the new processes are designed based on the process
redesign drivers. This may involve rework, redesign,
outsourcing or replacing of processes / sub processes.
The new processes thus defined are implemented, with IT
enablement (in most cases). The implementation phase may
require changes in the legal framework governing the
processes, and change management efforts to smoothen the
roll-out.
|
|
Approach to GPR
in MWRD |
Special GPR Workshop was organised for selected 32 officers
of MWRD working at various levels including Executive
Engineer, Deputy Engineers and Sectional Engineers having
rich experience in the field of construction and management
of Water Resources Projects. The details of this workshop is
given below-
1) GPR Workshop at Pune:
Special GPR workshop was organized at Pune for 32
officers from 7th Oct to 11 Oct 2013 in collaboration with
NISG. The course was inaugurated by Mr. T. N. Munde, e-Jalseva
Project Director and coordinated by Mr. Pravin Kolhe. This
is first attempt to understand concept of GPR and apply it
for the processes related to MWRD.
2) Methodology:
It was planned to first understand the GPR concepts and
apply those concepts in the process on which group is
working. First step to start with is preparation of “As Is”
Process Maps & its validation from seniors. Four Field
Mapping Template is used for mapping processes and then
process analysis is carried out in next 3 month in
co-ordination with Mr. Pravin Kolhe, Executive Engineer and
Wg Cdr A. K. Srinivas (Retd) who is working as consultant in
Project Management office, Pune. Then “To Be” maps will be
prepared, which will be validated from senior authorities in
a brain storming session. Once formal acceptance for To Be
maps is obtained from Government, the same will be developed
by the developer and incorporated in e-Jalseva with a
release of Version 2. The changes in the existing
methodologies and processes is expected in GPR and in order
to achieve that it is necessary to amend some rules and
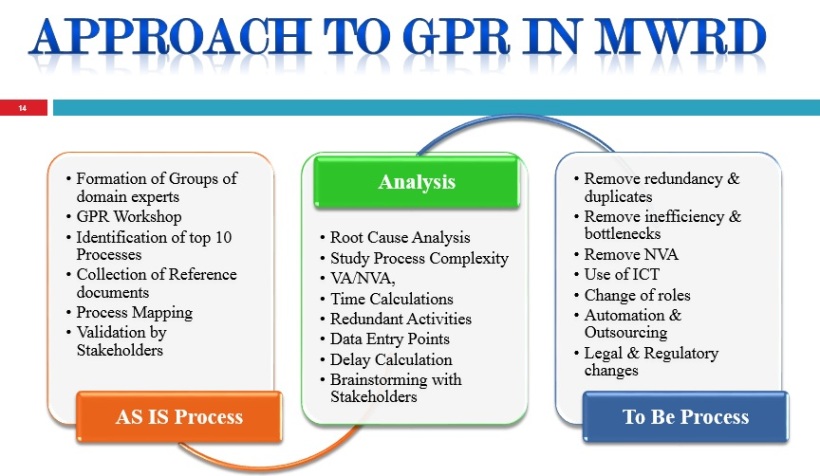
regulations. Following picture depicts the brief of approach
to GPR in MWRD-
3)
Selection of Processes and Formation of Groups:-
In
order to work for GPR, processes were identified using
service prioritization and keeping in view the process
complexity and its impact. Ten teams were formed which is
composed of domain experts from MWRD. The team members
selected for the GPR has extensive knowledge gained from
experience. The team is composed of lower and middle level
officer and details are available
here
In brief, approach to GPR followed in MWRD is represented
as-
|
|
Current Status |
|
STEP I]
Problem Identification: |
Problems in the existing e-Jalseva and manual processes were
identified by focus group workshops and during training to
end users. Further, requirements for various modules is
assessed by inviting suggestions and feedback from end
users. Complaints and expectations of stakeholders are
gathered. Thus, both pro-active & reactive methods for
problem identification are exercised and following problems
were prioritized-
Delay in service delivery due to centralization of power &
too many data entry points & manual touch points.
Non-standardization of service delivery process, which
causes rechecking and queries
Communication gap (interdepartmental & intra-departmental)
Non-standardization of proposals and certificates
Resource lacking-Manpower and fund
Poor record management & disintegrated information
storage.
Poor information retrieval
Delay caused due to travel time of files & outdated and
complex rules and procedure
De-centralized information storage and no mechanism for
updating it.
Vested interest
|
|
STEP II]
Vision & Objectives for GPR:
|
This is the common vision
for GPR, but each group is expected to precisely define
vision for GPR and state in quantifiable terms.
Objectives for GPR are mentioned below-
User Friendly & simplified procedures and rules by
adopting best practices and international standards.
Service Quality Monitoring & evaluation
Effective services and efficiency in terms of Cost, Time,
quality & Effort
Anytime anywhere service delivery with minimum human
intervention
Application of ICT at appropriate places
Simple, Moral, Accountable, Responsive & Transparent
(SMART) services
Citizen centric accessible services
In Brief,
Problem statement and Vision for GPR is presented below-

|
|
Step-III] Process Study &
Documentation (As Is Study) |
|
In this step, process owners and other stakeholders involved in
the workflow are identified by each group after gathering the
information available, brainstorming with other process owners
at Sub-division, division, circle, regional & ministerial level.
After gathering data, relevant acts, rules, manuals, GR related
to that process the processes were documented by the group. The
study of flow of process flow, actors involved in process,
policies, process stages are identified and mapped by group in
the form of four field mapping template. Through discussion
among domain experts the parameters such as VA/NVA, HoT, HoP,
TAT, DEP, etc. are calculated. The As Is process maps were
validated from senior officers of department.
At this stage all As Is Process maps of all groups are completed
and some maps are being validated form validation group,
specially created for that purpose. |
|
Step-IV]
Process Analysis |
|
The purpose of this step is to
conduct analysis of the selected processes at the macro and
micro level in order to identify bottlenecks and recommend
opportunities in delivery of services through eJalseva to
employees of MWRD and other stakeholders.
Root cause analysis of process issues and identification of root
causes is being carried out in a brainstorming session within
the group. The process efficiency is evaluated in terms of VA/NVA
activities. The process complexity is analyzed in terms of DEP &
HoP. The time calculation such as TAT, HoT etc. is done in order
to understand delay causing activities in a process.
|
|
Step-V]
Process Re-Engineering & Defining To Be Processes |
|
This is most crucial stage of
GPR where, future improved process is defined by eliminating or
automating the NVA and redundant activities. The solutions for
bottlenecks in As Is process is identified which leads to
reengineered process. Various alternative proposals were
evaluated in a discussion forum and best solution is selected by
the group in consultation with GPR experts. Again To-be
processes maps are evaluated and validated by seniors. The
necessary legal and regulatory changes needed for re-engineering
is also drafted. |
|
Step-VI]
Process Implementation & Validation |
|
This is last but most important step in GPR and as To Be
maps will be finalized and it will be given to developer for
creation in application software. In this project, this step
is yet to come, and it is planned that in 2014-2015, process
maps will be made available to Wipro Ltd for implementation
of IT system in e-Jalseva. The developed process will be
tested and audited, and once it is accepted, end users will
be trained to use re-engineering process, after issuing
legal and regulatory instructions.
|
|
|

