|
|
|
Background of
Maharashtra Water Resources Department (MWRD): |
|
Water is included in the state list (List 2)
of 7th schedule of the
Constitution of India except inter-state
rivers and river valleys. All activities
related to planning, development and
management of water resources are undertaken
by the respective states. All surface water
management related activities in the State
of Maharashtra are managed by Water
Resources Department (WRD). The Water
Resources Department (formerly known as
Irrigation Department) has a glorious
history of Irrigation and Water Management
over last 150 years. The MWRD came into
existence in 1867 as a separate organization
under Public Works Department during British
era. The state of Maharashtra came into
existence in the year 1960 after bifurcation
of old Bombay State into Maharashtra and
Gujarat. In the year 1960 the Public Works
Department was divided into Irrigation
Department and Building and Communication
Department. On 26 October 2004, Irrigation
Department is renamed as ‘Water Resources
Department’ resembling the importance of
water as a scare resource.
The Water Resources Department is entrusted
with survey, investigation, design,
construction, maintenance and management of
water resources and hydropower projects in
the river basins of the state. It also
undertakes command area development
programs, water drainage schemes, research
activities, training, dam safety, quality
control, hydrology data collection and
analysis, Kharbhumi schemes etc. Till 2012,
department constructed 3,332 water resources
project and thereby created water storage
capacity of 54,000 Mcum and irrigation
potential of 48.61 lakh ha across state.
|
|
Introduction to e-Jalseva: |
|
The Maharashtra Water Resources Department (MWRD)
is managing precious resource for the state
of Maharashtra and department has created
huge infrastructural projects. MWRD is
implementing innovative e-Governance project
named as “e-Jalseva”. Earlier, project was
started as component of MWSIP and named as
Integrated Computerized Information System (ICIS).
The 34 modules (refer annexure 1) from 8
functional area covering all major
activities of the department will lead to
less-paper working. e-Jalseva project will
ensure integrated, real time, one point
source of all water related information of
state as a whole. Further using BI tools the
optimum utilization of resources and
informed decision making is also possible.
The modules like Asset Management,
Litigation Management, Parliamentary
questions, training, accounts etc. are
helpful for other departments as well. The
capacity building initiatives through CIO
course and special e-Governance course of
IIM Indore are prominent initiatives carried
out by MWRD. The department owns the project
and dedicated officers are driving this
project. The success of project
implementation lies in top down and bottom
up approach adopted for sensitizing the
officers which is also unique in this
project. The in-house data digitization
initiatives and concept of eJalseva Month
viz. “eJalseva Abhiyaan” was as effective,
as it was innovative. The ‘panchsutri’ of
awareness, training, data digitization, data
validation and use of system were powerful
parameters for driving the initiative.
World Bank & Chief Secretary of Government
of Maharashtra have appreciated efforts
taken for this project and NISG has created
case study on this project for CIO course as
every aspect of this project is an
innovative initiative. This project is a
first initiative of its kind in the country
and department has devised a vision plan
including GIS maps, eMeasurement Book and
canal automation using SCADA system for
collecting data at source and automatic
passing of same to the stakeholders.
|
|
Problems, Issues &
Challenges |
1. All processes were simple & efficient
when originally designed. But Processes became
complex & inefficient with passage of time due
to-
· Addition of sub-processes to handle
exceptions
· Changes in environment and
· Increase in customer expectations
· Increase in volumes
· Changes in structure of department due
to formation of corporations
2. Duplication & dis-integrated approach of
data capturing leading to conflicting
information at various forums.
3. Timely availability of Information at
various levels. |
|
Benefits & Status: |
eJalseva was conceptualized to achieve the
following objectives:
· Better WR management with
real time data regarding availability & demand.
· To enable WRD to deliver
services, in more effective & client oriented
manner.
· To improve efficiency of
Administration.
· To exercise better
financial and budgetary control.
· To facilitate a
collaborative working culture.
· Capturing data where it is
generated & dissemination of data electronically
wherever & whenever required.
· Informed decision making
· Better work flow
management.
The Clarity PPM product suite is the main
stay COTS product used for developing the
ICIS application with web based front end.
It consists of forms, reports and work flow
mechanism to present the MIS of any module.
·
For a smooth roll out and successful
implementation of eJalseva, a dedicated
Project Management Office (PMO) has been
established at Pune under Superintending
Engineer, Koyna Design Circle in July2012.
PMO coordinates the activities of related
vendor management and procurement
management.
·
The PMO, comprising of about 9 officers
having departmental domain knowledge and 3
technical experts from PMO partner NISG,
aims to ensure sustained performance and
improvements to the e-Jalseva application in
the future. PMO provides technical advisory
and hand holding support to the field
officers during and after the roll out of
the system.
·
An integral part of any eGovernance Project,
Change Management (CM) has been an
instrumental tool for driving the acceptance
of the project among the WRD employees.
Focusing primarily on Training and
Communication strategies and their
implementation, the PMO has carried out
numerous awareness workshops and trainings
to drive the project. To train the
application, a Master Trainer (MT) / Trainer
of Trainers (ToT) approach has been adopted.
·
As of now about 15000 plus man days of
trainings have been imparted by the PMO. 800
plus Master Trainers have been trained so
far.
·
Under Project Management activities, all 34
modules went live in a phased manner.
Initially, a total of 42 pilot projects were
entered in the system across six
administrative divisions in Maharashtra.
Network connectivity for the project is
being provided by BSNL through VPN over
broadband. Network connectivity at 645
locations is already completed by BSNL .
User level hardware (Lot I) was delivered to
all WRD offices and installation got
completed at around 700 locations also
training for the hardware, Linux operating
system and Open Office is completed.
·
Till date around 3700 plus irrigation
projects have been entered in the module M8
of the system which is the master data and
provides inputs to all the other modules.
For Non Irrigation (NI) assessment data,
related to NI customers and Farmers, the
Master data has also been entered in module
M19 of the system and 6356 customers for
Non Irrigation are created and validated.
Also more than 10,03,190 farmers data on
various projects is entered. Online
submission of Monthly accounts from module
M24 of the system to Accountant General,
Nagpur through web service has already been
achieved successfully since January 2014.
This is being done by 137 divisions now
being entered through the system only.
·
Around 150 GB data of textual data is
present in the system. In addition another
50 GB of data in form of attachments has
been input by the departmental.
|
|
Project Milestones |
|
#
|
Milestone
|
Proposed / Achieved timeline
|
Status
|
|
1.
|
ICIS Strategy & Roadmap
|
March 2007
|
Completed
|
|
2.
|
As Is study
|
Aug 2007
|
Completed
|
|
3.
|
To be study
|
March 2008
|
Completed
|
|
4.
|
RFP for selection of SI
|
Nov 2008
|
Completed
|
|
5.
|
Selection of SI
|
July 2009
|
Completed
|
|
6.
|
Inception report & project plan
|
Oct 2009
|
Completed
|
|
7.
|
RGT template finalisation
|
March 2010
|
Completed
|
|
8.
|
Requirement gathering
|
Oct 2010
|
Completed
|
|
9.
|
SRS
|
Nov 2010
|
Completed
|
|
10.
|
SDD
|
Dec 2010
|
Completed
|
|
11.
|
ICIS Application development
|
June 2011
|
Completed
|
|
12.
|
Testing (UAT)
|
Dec 2011
|
Completed
|
|
13.
|
Data digitisation for pilot
|
Aug 2012
|
Completed
|
|
14.
|
Selection of hardware vendors
|
June 2012
|
Completed
|
|
15.
|
Hardware deployment(Lot I)
|
Jan 2013
|
Completed
|
|
|
(Lot II)
|
Jan 2014
|
Completed
|
|
16.
|
Last mile network connectivity
|
September 2014
|
Ongoing
|
|
17.
|
Server setup at SDC, Mumbai
|
Mar 2013
|
completed
|
|
18.
|
Third Party Security audit
|
Jan 2013
|
Completed
|
|
19.
|
Training
|
Mar 2013
|
Completed
|
|
20.
|
Application migration to SDC
|
April 2013 (Total installation)
|
Completed
|
|
21.
|
Pilot I launch
|
Sept 2012
|
Completed
|
|
22.
|
Pilot II launch
|
Feb 2013
|
Completed
|
|
23.
|
Pilot III launch
|
Mid June 2013
|
Completed
|
|
24.
|
Go Live
|
May 2013
|
Completed
|
|
25.
|
Operational acceptance
|
|
Ongoing
|
ICIS projects'
procurement and training components'
implementation are completed for by March
2014 as per above status. Post
implementation completion all the
infrastructure procured and applications
developed will be under 3 years warranty.
The customized e Jalseva application will
also have additional 3 years post warranty
support from the System Integrator.
|
|
Impact of e-Jalseva: |
|
e-Jalseva
is ambitious eGovernance initiative of
Maharashtra Water Resources Department
which was conceptualized as Management
Information System and later on it was
re-designed and implemented as comprehensive
integrated e-governance project covering 726
offices of department. Employees, citizens,
farmers, water user associations,
industries, contractors, project affected
persons, other government departments, media
etc. are the major stakeholders of the
department. Although e-Jalseva is designed
so as to fulfill major requirements of these
stakeholders, at this stage of
implementation, biggest beneficiary of the
system is its employees.
Currently, e-Jalseva is at
transaction stage where electronic delivery
of some processes is achieved and road map
is prepared and being implemented in a
phased manner in order to progress to
Transformation stage, where there will be
joined-up services and all transactions will
be carried out through system only.
Following are the tangible benefits observed
after use of e-Jalseva-
1)
Centralized
unified Database:
Earlier data was available at or near
source. Whenever policy makers required some
data, letter is sent to lower level office
asking to submit data in prescribed format.
When data is received, often it was observed
that it was inconsistent and not matching
with earlier record entries. Even some time
data was not made available due to various
reasons. E-Jalseva helped to create central
database which updated by the owner of data
and validated by superior officer and thus
instantaneously data is made available for
decision making.
2)Saving
in Time, effort and cost:
Approximately 15
days to 2 months were required to gather the
data from field office to Mantralaya. E-Jalseva
acts as speedy route for commination between
various levels of authorities including
vertical and horizontal data movement.
3)Record
Management and Documentation:
Huge amount of information is generated
while constructing and managing water
resources projects, which if not captured
gets vanished. E-Jalseva provided platform
for one-stop solution for all records and
documentation.
4)
Empowerment
of Employee:
The system helped many employees to be
acquire knowledge about ICT and some of them
become expert in computer and started
solving problems faced by other employees.
MWRD decided to digitize all its data
through its employees only. It was crucial
decision, but after proper training the idea
worked successfully. This helped in getting
in-depth understanding of system to the
employee as well as cost is saved as
outsourcing is avoided.
5)
Infrastructure Development:
Laptops, Desktops, printers, LAN, Network
connectivity etc. is provided as a part of
e-Jalseva empowered infrastructure
facilities in the offices of MWRD. Some
offices were remotely located were not
connected with Broadband internet connection
are now connected to world of internet.
6)
Master Trainers:
This concept was efficiently implemented for
inculcating training to the employees. The
human resource capacity of MWRD is
approximately 50,000. It is not possible to
train all employees in short span of 2 year.
Therefor concept of Train the Trainer is
adopted and selected officers were trained
to acquire certain level of understanding of
e-Jalseva and they conducted training
session in their offices at filed level.
They also acted as help desk for many
employees.
7)
Capacity Building: Till date about
15,000 plus man days training is provided
within the department. Training, workshops,
discussion forum etc were organized as and
when required and on regular basis. Nearly
800 master trainer along with Change
Management division of PMO office worked
hard to empower employees of MWRD.
As already mentioned,
current version of e-Jalseva is focused on
its employees (G2E) l. In coming time, it is
planned to bring out next version of e-Jalseva
catering the more to the needs of citizens,
industries and contractors. Then impact
assessment on these stakeholders will be
studied.
|
|
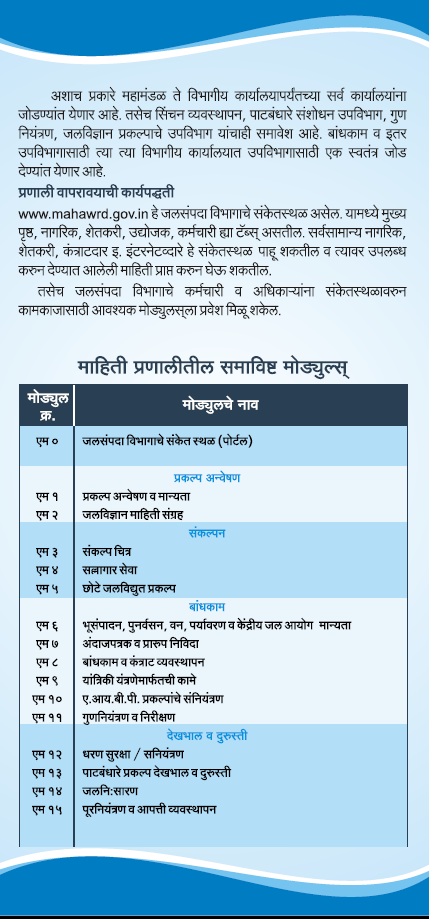
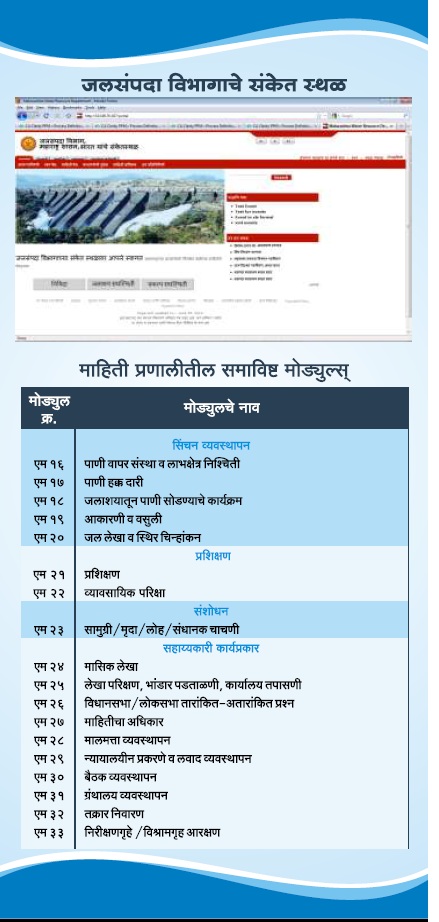
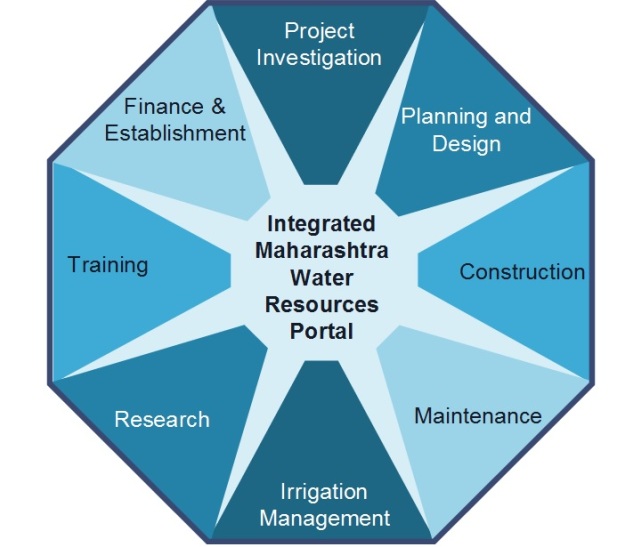
List of Modules &
Functionalities of e-Jalseva |
|
Functional Area
|
Module
|
Functionality in brief
|
|
Portal
|
M0
|
Portal
|
Unified WRD
Portal, centralised access to
ICIS
|
|
Project
Investigation
|
M1
|
Project
Investigations
|
Creation of a
Project. Information about the
project would be available to
all modules
|
|
M2
|
Hydrological
Data
|
Water
availability and decimation of
river and rain guage data
|
|
Designing
|
M3
|
Designing
|
Finalising
Annual Design Program
|
|
M4
|
Consultancy
|
Facilitate
tracking of consultancy work
|
|
M5
|
Small Hydro
Projects
|
Facilitate
monitoring of SHPs and vetting
of TEFR
|
|
Construction
|
M6
|
Land
Acquisition
|
LA proposal,
clearances, tracking of LA &
rehabilitation status
|
|
M7
|
Estimates and
DTP
|
Estimates for
works and draft tender papers
|
|
M8
|
Construction
, contract management & Progress
Monitoring
|
Projects and
Contractors database and
physical and financial
monitoring
|
|
Construction
|
M9
|
Mechanical
Organization
|
Earthwork &
Canal Cleaning execution and
Gate Manufacturing
|
|
M10
|
Monitoring
Projects under AIBP
|
Proposal for
loan assistance under AIBP and
payment of bills
|
|
M11
|
Inspection &
Quality Control
|
Program for
inspection of work and quality
control procedure
|
|
Maintenance
|
M12
|
Dam Safety /
Monitoring
|
Dam
inspection, gate inspection &
annual health report
|
|
M13
|
Maintenance
of Completed Projects
|
Annual
Maintenance plan and proposal
for project maintenance
|
|
M14
|
Land
Reclamation
|
Construction
of drainage schemes for land
reclamation
|
|
M15
|
Flood Control
& Disaster Management
|
Compilation &
Dissemination of flood data
|
|
Irrigation
Management
|
M16
|
Delineation
of Command and WUAs
|
Formation of
Water User Associations and
delineation of command
|
|
M17
|
Water
Entitlement
|
Issuing
entitlements and monitoring of
usage; transfer of entitlements
|
|
M18
|
Water Release
Schedule
|
Collection of
water demand, issuance of passes
and preparation of rotation
program
|
|
M19
|
Assessment,
Billing and Recovery
|
Water usage
billing and recovery
|
|
M20
|
Water
Auditing and Benchmarking
|
Account of
water utilization, water account
preparation, water auditing and
benchmarking
|
|
Training
|
M21
|
Training
|
Annual
Training Program and selection
of trainees
|
|
M22
|
Professional
Exam
|
Exam
calendar, exam applications and
hall tickets
|
|
Research
|
M23
|
Material
/Soil / Steel Testing
|
Cost estimate
for testing, testing report,
client list & feedback
|
|
Support
functions/finance &
establishment
|
M24
|
M24:Accounts
Reconciliation with Treasury &
AG
|
Maintaining
monthly accounts and
reconciliation
|
|
M25
|
Inspection /
Audit Report Compliance
|
Compliance of
audit para
|
|
M26
|
Assembly /
Parliamentary Questions
|
Questions
Reply & Assurance Monitoring
|
|
M27
|
RTI
|
RTI
application compliance
|
|
M28
|
Asset
Management
|
Register and
inventory of various assets
|
|
M29
|
Litigation
Management
|
Record of
court cases
|
|
M30
|
Meeting
Management
|
Scheduling
meetings and circulating minutes
|
|
M31
|
Library
Management
|
Library
database, requisition and
issuing of books
|
|
M32
|
Grievance
Redressal
|
Registering
complaint and track resolution
|
|
M33
|
Reservation
of Inspection Bungalows
|
Bungalow
database and rooms reservation
|
|
|
e-Governance Road Map
for MWRD: |
|
The enthusiasm and
acceptance of existing e-Jalseva encouraged
PMO to prepare Vision 2020 report which
includes several ICT based innovative
initiatives which will fulfill the
requirements of all stakeholders and achieve
sustainable water management in a state. The
e-Governance Roadmap is prepared to provide
a framework for more coordinated focus for
the implementation of ICT systems as part of
enabling the MWRD’s development objectives
and streamlining the implementation of the
e-Governance Strategy for Vision 2020. The
roadmap also sets specific goals and targets
whose achievement will not only deliver
better services to more citizens, but will
also result in cost saving in the delivery
of services while enabling many new types of
services to be created as part of the water
and irrigation sector development. The
Vision 2020 roadmap includes-
a)
Enhancements to e-Jalseva:-
1) GPR of basic modules
---Already started
2) Improved user interface &
simpler forms--- Ongoing activity
3) Enhanced reporting and
dashboard features using business
intelligence tools
4) Online estimate preparation
functionality including DSR, rate analysis
etc.
5) e-Measurement Book, billing
and contracts management
6) Online submission of monthly
accounts
7) Information System for Water
Users Associations for enhancing
participation
b)
Mobile
Based Services
1) Flood alerts
2) Meetings/reminder alerts to
concern officers
3) Water supply, billing and
related information communication
4) Reservoir storage data input
from field staff
5) Geo-time stamped photographs
for documentation for work in progress
c)
Remote
Sensing and GIS-based Decision Support
System
1) Support for Water Management &
Irrigation management
2) Mapping State Water Plan
vis-à-vis created and balanced water in a
state
3) Mapping of water bodies using
GIS maps and remote sensing data
4) Mapping of canal network &
structures
5) Command area map and catchment
area map
6) Mapping of irrigation
potential achieved based on satellite data
as compared to actual
7) Impact assessment of
irrigation projects using land-use
parameters
8) Flood line maps
d)
Other
Key Components
1) Development of HRM related
module consistent with requirements of MWRD.
2) GPR & Reforms
3) Enablement of service delivery
through CSC like Maha e-Seva Centre
4) Integration with e-Office
5) Integration with e-Payment
Gateway payments
6) Integration with GRAS of
Government of Maharashtra
e)
Provisioning of ICT infrastructure:-
1) Department wide e-mail
solution
2) Video-conferencing solution
3) LAN, WAN and VPN connectivity
4) Appropriate mobile devices as
per technological requirements.
f)
Integration with Other eGov Project
1) Integration with BDS
2) Integration with the Sevaarth
3) e-Service Book
4) Land Records Information
System
5) UID/ Aadhaar
6) Portals developed by Central
Water Commission and Ministry of Water
Resource
7) Agriculture MMP of the
Department of Agriculture, Government of
India
8) State-wide e-Procurement &
e-Auction system
g)
Other
major long Term initiatives
1) Land Use Mapping system
2) SCADA based Data Acquisition
System for Canal Automation
3) Decision Support System for
Water Management Modeling System-BI Tools
4) Implementation of cutting-edge
ICT-based improvements in the water sector.
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
|
Resources Related to eJalseva Project of
Maharashtra Water Resources Department
(earlier Integrated Computerized
Information System)
|
|
e-Jalseva (earlier ICIS) Newsletters
|
|
VOLUME-1
|
VOLUME-2
|
|
ICIS Bulletin:- May-2011-Vol-1, Issue-01
|
ICIS Bulletin:- May-2012-Vol-2, Issue-01
|
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Jun-2011-Vol-1, Issue-02
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Jun-2012-Vol-2, Issue-02
|
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Jul-2011-Vol-1, Issue-03
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Jul-2012-Vol-2, Issue-03
|
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Aug-2011-Vol-1, Issue-04
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Aug-2012-Vol-2, Issue-04
|
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Sep-2011-Vol-1, Issue-05
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Sep-2012-Vol-2, Issue-05
|
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Oct-2011-Vol-1, Issue-06
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Oct-2012-Vol-2, Issue-06
|
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Nov-2011-Vol-1, Issue-07
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Nov-2012-Vol-2, Issue-07
|
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Dec-2011-Vol-1, Issue-08
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Dec-2012-Vol-2, Issue-08
|
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Jan-2012-Vol-1, Issue-09
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Jan-2013-Vol-2, Issue-09
|
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Feb-2012-Vol-1, Issue-10
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Feb-2013-Vol-2, Issue-10
|
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Mar-2012-Vol-1, Issue-11
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Mar-2013-Vol-2, Issue-11
|
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Apr-2012-Vol-1, Issue-12
|
ICIS Bulletin:- Apr-2013-Vol-2, Issue-12
|
|
|
|
|
VOLUME-3
|
VOLUME-4
|
|
e-Jalseva Bulletin:- May-2013-Vol-3,
Issue-01
|
e-Jalseva
Bulletin:- May-2014-Vol-4, Issue-01
|
|
e-Jalseva Bulletin:- Jun-2013-Vol-3,
Issue-02
|
e-Jalseva
Bulletin:- Jun-2014-Vol-4, Issue-02
|
|
e-Jalseva Bulletin:-
Jul-2013-Vol-3, Issue-03
|
e-Jalseva
Bulletin:- Jul-2014-Vol-4, Issue-03
|
|
e-Jalseva Bulletin:- Aug-2013-Vol-3,
Issue-04
|
e-Jalseva
Bulletin:- Aug-2014-Vol-4, Issue-04
|
|
e-Jalseva Bulletin:- Sep-2013-Vol-3,
Issue-05
|
e-Jalseva
Bulletin:- Sept-2014-Vol-4, Issue-05
|
|
e-Jalseva Bulletin:- Oct-2013-Vol-3,
Issue-06
|
e-Jalseva
Bulletin:- Oct-2014-Vol-4, Issue-06
|
|
e-Jalseva Bulletin:- Nov-2013-Vol-3,
Issue-07
|
e-Jalseva
Bulletin:- Nov-2014-Vol-4, Issue-07 |
|
e-Jalseva
Bulletin:- Dec-2013-Vol-3, Issue-08
|
e-Jalseva
Bulletin:- Dec-2014-Vol-4, Issue-08
|
|
e-Jalseva
Bulletin:- Jan-2014-Vol-3, Issue-09
|
e-Jalseva
Bulletin:- Jan-2015-Vol-4, Issue-09 |
|
e-Jalseva
Bulletin:- Feb-2014-Vol-3, Issue-10
|
e-Jalseva
Bulletin:- Feb-2015-Vol-4, Issue-10
|
|
e-Jalseva
Bulletin:- Mar-2014-Vol-3, Issue-11
|
|
|
e-Jalseva
Bulletin:- Apr-2014-Vol-3, Issue-12
|
|
|
|
|

